| City | River | Country |
|---|---|---|
| Adelaide | Torrens | Australia |
| Al-Cairo | Nile | Egypt |
| Alexandria | Nile | Egypt |
| Amsterdam | Amsel | Netherlands |
| Ankara | Kazil | Turkey |
| Baghdad | Tigris | Iraq |
| Bangkok | Chao Praya | Thailand |
| Basra | Elupharates and Tigris | Iraq |
| Belgrade | The confluence of the Sava and Danube | Serbia |
| Berlin | Spree and Havel | Germany |
| Bonn | Rhine | Germany |
| Bogota | Bogota | Colombia |
| Bristol | Avon | United Kingdom |
| Budapest | Danube | Hungary |
| Budapest | Danube | Hungary |
| Buenos Aires | Río de la Plata | Argentina |
| Buenos Alres | Laplata | Argentina |
| Cairo | Nile | Egypt |
| Canton | Si-Kiang | China |
| Caracas | Guaire | Venezuela |
| Chittagong | Maiyani | Bangladesh |
| Cologne | Rhine | Germany |
| Cologne | Rhine | Germany |
| Dandzing | Vistula | Germany |
| Delhi | Yamuna | India |
| Dresden | Elbe | Germany |
| Dublin | Liffey | Ireland |
| Hamburg | Elbe | Germany |
| Haridwar | Ganga | India |
| Hong Kong | Lam Tsuen | China |
| Jakarta | Ci Liwung | Indonesia |
| Kabul | Kabul | Afghanistan |
| Karachi | Indus | Pakistan |
| Khartoum | The confluence of Blue & White Nile | Sudan |
| Kolkata | Hooghly | India |
| Lahore | Ravi | Pakistan |
| Leningrad | Neva | Russia |
| Lisbon | Tagus | Portugal |
| Liverpool | Messey | England |
| London | Thames | England |
| Madrid | Manzanares | Spain |
| Melbourne | Yarra | Australia |
| Montreal | The confluence of the Saint Lawrence and Ottawa | Canada |
| Moscow | Moskva | Russia |
| Nanking | Yangtse | China |
| New Orleans | Mississippi | USA |
| New York | Hudson | USA |
| Ottawa | Ottawa | Canada |
| Paris | Seine | France |
| Perth | Swan | Australia |
| Philadelphia | Delaware | USA |
| Prague | Vitava | Czech Republic |
| Quebec | St. Lawrence | Canada |
| Rome | Tiber | Italy |
| Rotterdam | New mass | The Netherlands |
| Saint Luis | Mississippi | USA |
| Seoul | Han River | South Korea |
| Santiago | Mapocho | Chile |
| Shanghai | Yangtse | China |
| Sidney | Darling | Australia |
| Stalingrad | Volga | Russia |
| Tokyo | Arakawa | Japan |
| Vienna | Danube | Austria |
| Warsaw | Vistula | Poland |
| Washington D.C. | Potomac | USA |
| Yangon | Irrawaddy | Myanmar |
Sunday, 30 April 2023
नदी के किनारे बसे शहर
Wednesday, 8 March 2023
Windows Shortcuts
Here's the full list of keyboard short-cuts for Windows 10 - all the Windows 10 keyboard shortcuts you need to know
Keyboard shortcut → Action
Windows key → Open or close Start Menu.
Windows key + A → Open Action center. (Notification Bar & Settings)
Windows key + B - Jump to Task Bar (Right Toggle key)
Windows key + C → Open Cortana in listening mode. (Voice Typing) In Window 10.
Windows key + D → Display or hide the desktop.
Windows key + E → Open File Explorer.
Windows key + F → Feedback Hub (to Microsoft)
Windows key + G → Open Game bar when a game is open. (X-Box Record Screen).
Windows key + H → Voice Typing (Acess to Share Charms In Window 8)
Windows key + I → Open Window Settings.
Windows key + J →
Windows key + K → Open the Connect quick action. (to Connect Wireless Divice)
Windows key + L → Lock your PC or switch accounts.
Windows key + M → Minimize all Programs.
Windows key + N → No
Windows key + P → Presentation Display Mode.
Note:- जब हम अपने कंप्यूटर में कोई प्रॉजेक्टर (Projector) या दो मॉनिटर (Monitor) का उपयोग करना चाहते है तब इस Shortcut Key ( Windows + P) की मदद से हम हमारे कम्प्युटर की स्क्रीन (screen) को प्रॉजेक्टर (Projector) या दूसरे मॉनिटर (Monitor) के साथ प्रबंधन (Management) करते है।
Windows key + U → Open Clipboard.
Windows key + Shift + Q → Quick Assist (It helps to connect one computer to other)
Windows key + R → Open Run dialog box.
Windows key + S → Open Search.
Windows key + T → Jump to Taskbar.
Note:- अपने कंप्यूटर के टास्कबार (Taskbar) पे पिन एप्लिकेशन (Pinned Application) को एक एक करके चुनने (select) के लिए Shortcut Key: Windows + T का उपयोग कर सकते है।
Windows key + U → Open Ease of Access Center.(Display Setting).
Windows key + U → Open Clipboard.
Windows key + V → Open Clipboard.
Windows key + W → Open Whiteboard.
Windows key + X → Open Quick Link menu.(you Will Get some usable tools there)
Note:- अपने कंप्यूटर के मोबिलिटी सेंटर (Mobility Center) पे जाने के लिए इस Shortcut Key: Windows + X का इस्तेमाल कर सकते है।
Windows key + Number → Open the app pinned to the taskbar in the position indicated by the number.
Windows key + Left arrow key → Snap app windows left.
Windows key + Right arrow key → Snap app windows right.
Windows key + Up arrow key → Maximize app windows.
Windows key + Down arrow key → Minimize app windows.
Windows key + Comma → Temporarily peek at the desktop.
Windows key + Ctrl + D → Add a virtual desktop.
Windows key + Ctrl + Left or Right arrow → Switch between virtual desktops.
Windows key + Ctrl + F4 → Close current virtual desktop.
Windows key + Enter → Open Narrator.
Windows key + Home → Minimize all but the active desktop window (restores all windows on second stroke).
Note:-Shortcut Key (Windows + Home) का इस्तेमाल करके आप विंडोज मे सारे एप्लिकेशन को मिनिमाइज़ (Minimize) या रेस्टोर (Restore) कर सकते हो।
Windows key + PrtScn → Capture a screenshot and save in Screenshots folder.
Windows key + Shift + Up arrow → Stretch the desktop window to the top and bottom of the screen.
Windows key + Tab → Open Task view. (Switch from One Window to another)
Windows key + "+" key → Zoom in using the magnifier.
Windows key + "-" key → Zoom out using the magnifier.
Thursday, 8 December 2022
File Extension
| File Extension | File Type |
|---|---|
| .AIFF or .AIF | Audio Interchange File Format |
| .AU | Basic Audio |
| .AVI | Multimedia Audio/Video |
| .BAT | PC batch file |
| .BMP | Windows BitMap |
| .CLASS or .JAVA | Java files |
| .CSV | Comma separated, variable length file (Open in Excel) |
| .CVS | Canvas |
| .DBF | dbase II, III, IV data |
| .DIF | Data Interchange format |
| .DOC or .DOCX | Microsoft Word for Windows/Word97 |
| .EPS | Encapsulated PostScript |
| .EXE | PC Application |
| .FM3 | Filemaker Pro databases (the numbers following represent the version #) |
| .GIF | Graphics Interchange Format |
| .HQX | Macintosh BinHex |
| .HTM or .HTML | Web page source text |
| .JPG or JPEG | JPEG graphic |
| .MAC | MacPaint |
| .MAP | Web page imagemap |
| .MDB | MS Access database |
| .MID or .MIDI | MIDI sound |
| .MOV or .QT | QuickTime Audio/Video |
| .MTB or .MTW | MiniTab |
| Acrobat -Portable document format | |
| .P65 .T65 | PageMaker (the numbers following represent the version #) P=publication, T=template |
| .PNG | Portable Network Graphics |
| .PPT or .PPTX | PowerPoint |
| .PSD | Adobe PhotoShop |
| .PSP | PaintShop Pro |
| .QXD | QuarkXPress |
| .RA | RealAudio |
| .RTF | Rich Text Format |
| .SIT | Stuffit Compressed Archive |
| .TAR | UNIX TAR Compressed Archive |
| .TIF | TIFF graphic |
| .TXT | ASCII text (Mac text does not contain line feeds--use DOS Washer Utility to fix) |
| .WAV | Windows sound |
| .WK3 | Lotus 1-2-3 (the numbers following represent the version #) |
| .WKS | MS Works |
| WPD or .WP5 | WordPerfect (the numbers following represent the version #) |
| .XLS or .XLSX | Excel spreadsheet |
| .ZIP | PC Zip Compressed Archive |
Friday, 29 July 2022
Full Form of computers
| COMPUTER - | Common Operating Machine Purposely Used for Technological and Educational Research |
| ROM | Read-Only Memory |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| URL | Uniform Resource Locator |
| USB | Universal Serial Bus |
| VIRUS | Vital Information Resource Under Siege |
| TCP | Transmission Control Protocol |
| UPS | Uninterruptible Power Supply |
| SATA | Serial Advanced Technology Attachment |
| RAM | Random Access Memory |
| SMPS | Switched-Mode Power Supply |
| CD | Compact Disc |
| DVD | Digital Versatile Disc |
| CRT | Cathode Ray Tube |
| DEC | Digital Equipment Corporation |
| SAP | System Application and Products |
| PNG | Portable Network Graphics |
| IP | Internet Protocol |
| GIS | Geographical Information system |
| DDS | Digital Data Storage |
| CAD | Computer-Aided Design |
| ACPI | Advanced Configuration and Power Interface |
| AGP | Accelerated Graphics Port |
| APM | Advanced Power Management |
| APIPA | Automatic Private Internet Protocol Addressing |
| HTTP | HyperText Transfer Protocol |
| HTTPS | HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure |
Tuesday, 19 July 2022
Computer
Topic A: Computer generations
Basic Terms

– an electronic device that controls the flow of electrons in a vacuum. It used as a switch, amplifier, or display screen in many older model radios, televisions, computers, etc.

– an electronic component that can be used as an amplifier or as a switch. It is used to control the flow of electricity in radios, televisions, computers, etc.
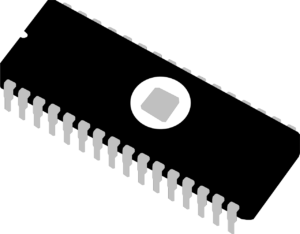
– a small electronic circuit printed on a chip (usually made of silicon) that contains many its own circuit elements (e.g. transistors, diodes, resistors, etc.).

– an electronic component held on an integrated circuit that contains a computer’s central processing unit (CPU) and other associated circuits.

– It is often referred to as the brain or engine of a computer where most of the processing and operations take place (CPU is part of a microprocessor).

– a cylinder coated with magnetic material, on which data and programs can be stored.
– uses arrays of small rings of magnetized material called cores to store information.

– a low-level programming language comprised of a collection of binary digits (ones and zeros) that the computer can read and understand.
Assembly language is like the machine language that a computer can understand, except that assembly language uses abbreviated words (e.g. ADD, SUB, DIV…) in place of numbers (0s and 1s).
 – a physical device that is used to store data, information and program in a computer.
– a physical device that is used to store data, information and program in a computer.
– an area of computer science that deals with the simulation and creation of intelligent machines or intelligent behave in computers (they think, learn, work, and react like humans).
First Generation of Computers
Classification of generations of computers
The evolution of computer technology is often divided into five generations.
| Generations of computers | Generations timeline | Evolving hardware |
|---|---|---|
| First generation | 1940s-1950s | Vacuum tube based |
| Second generation | 1950s-1960s | Transistor based |
| Third generation | 1960s-1970s | Integrated circuit based |
| Fourth generation | 1970s-present | Microprocessor based |
| Fifth generation | The present and the future | Artificial intelligence based |
The main characteristics of first generation of computers (1940s-1950s)
- Main electronic component – vacuum tube

- Main memory – magnetic drums and magnetic tapes
- Programming language – machine language
- Power – consume a lot of electricity and generate a lot of heat.

- Speed and size – very slow and very large in size (often taking up entire room).
- Input/output devices – punched cards and paper tape.
- Examples – ENIAC, UNIVAC1, IBM 650, IBM 701, etc.
- Quantity – there were about 100 different vacuum tube computers produced between 1942 and1963.
Second Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of second generation of computers (1950s-1960s)

Main electronic component – transistor
- Memory – magnetic core and magnetic tape / disk
 Programming language – assembly language
Programming language – assembly language- Power and size – low power consumption, generated less heat, and smaller in size (in comparison with the first generation computers).
- Speed – improvement of speed and reliability (in comparison with the first generation computers).
- Input/output devices – punched cards and magnetic tape.
- Examples – IBM 1401, IBM 7090 and 7094, UNIVAC 1107, etc.
Third Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of third generation of computers (1960s-1970s)
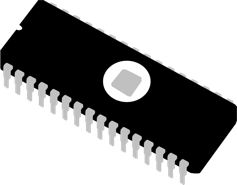 Main electronic component – integrated circuits (ICs)
Main electronic component – integrated circuits (ICs)- Memory – large magnetic core, magnetic tape / disk
- Programming language – high level language (FORTRAN, BASIC, Pascal, COBOL, C, etc.)

- Size – smaller, cheaper, and more efficient than second generation computers (they were called minicomputers).
- Speed – improvement of speed and reliability (in comparison with the second generation computers).
- Input / output devices – magnetic tape, keyboard, monitor, printer, etc.

- Examples – IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP-11, UNIVAC 1108, etc.
Fourth Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of fourth generation of computers (1970s-present)
 Main electronic component – very large-scale integration (VLSI) and microprocessor.
Main electronic component – very large-scale integration (VLSI) and microprocessor.- VLSI– thousands of transistors on a single microchip.
- Memory – semiconductor memory (such as RAM, ROM, etc.)
- RAM (random-access memory) – a type of data storage (memory element) used in computers that temporary stores of programs and data (volatile: its contents are lost when the computer is turned off).
 ROM (read-only memory) – a type of data storage used in computers that permanently stores data and programs (non-volatile: its contents are retained even when the computer is turned off).
ROM (read-only memory) – a type of data storage used in computers that permanently stores data and programs (non-volatile: its contents are retained even when the computer is turned off).
- Programming language – high level language (Python, C#, Java, JavaScript, Rust, Kotlin, etc.).
- A mix of both third- and fourth-generation languages
- Size – smaller, cheaper and more efficient than third generation computers.
- Speed – improvement of speed, accuracy, and reliability (in comparison with the third generation computers).
 Input / output devices – keyboard, pointing devices, optical scanning, monitor, printer, etc.
Input / output devices – keyboard, pointing devices, optical scanning, monitor, printer, etc.
- Network – a group of two or more computer systems linked together.
- Examples – IBM PC, STAR 1000, APPLE II, Apple Macintosh, etc.

Fifth Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of fifth generation of computers (the present and the future)
 Main electronic component: based on artificial intelligence, uses the Ultra Large-Scale Integration (ULSI) technology and parallel processing method.
Main electronic component: based on artificial intelligence, uses the Ultra Large-Scale Integration (ULSI) technology and parallel processing method.- ULSI – millions of transistors on a single microchip
- Parallel processing method – use two or more microprocessors to run tasks simultaneously.
- Language – understand natural language (human language).
- Power – consume less power and generate less heat.
- Speed – remarkable improvement of speed, accuracy and reliability (in comparison with the fourth generation computers).
- Size – portable and small in size, and have a huge storage capacity.
 Input / output device – keyboard, monitor, mouse, trackpad (or touchpad), touchscreen, pen, speech input (recognise voice / speech), light scanner, printer, etc.
Input / output device – keyboard, monitor, mouse, trackpad (or touchpad), touchscreen, pen, speech input (recognise voice / speech), light scanner, printer, etc.- Example – desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc.
Saturday, 26 June 2021
पहाड़िया विद्रोह|Paharia Revolt|Jharkhand GK PDF|
Sunday, 13 June 2021
Jharkhand GK MCQ 1
1. झारखंड के किन जिलों की सीमा किसी राज्य से नही लगती?
खूंटी और लोहरदग्गा
2. राजमहल पहाड़ी में किस खनिजों की भंडारण का पता चला है?1q
3. झारखंड राज्य में सर्वाधिक वर्षा प्राप्त करने वाला जिला?
4. झारखंड के किस क्षेत्र को पश्चिम पठार भी कहा जाता है?
5. झारखण्ड का दूसरा सबसे ऊंचा पाट कौन सा है?
6. झारखंड मे कितना भूमि पर कृषि कार्य होता है?
7. झारखंड की दूसरी प्रमुख फसल कौन सी है?
8. झारखंड में आधुनिक कृषि तकनीक का उपयोग ठीक तरह से नही होने का प्रमुख कारण क्या है?
9. झारखंड में मक्का का सर्वाधिक उत्पादन किस जिला में होता है?
10. ढाल विद्रोह के दौरान अंग्रेजो ने जगनाथ ढाल को अपदस्थ कर किसी धालभूम का राजा बना दिया था?
11. अंग्रेज़ो ने जगनाथ ढाल को अंग्रेज़ो ने राजा कब स्वीकार किया?
12. पुनः जगनाथ ढाल को राजा स्वीकारने के बदले कितना टैक्स देना तय हुवा?
13. मानभूम और बडाभूम क्षेत्रों में चुआर विद्रोह का नेतृत्व किसने किया?
14. किस विद्रोह को चेरो विद्रोह का पूरक माना जाता है?
15.भोगता विद्रोह किस क्षेत्र में घटित हुवा?
16. भुगता विद्रोह में जयनाथ सिंह के पराजय होने के बाद किसे पलामू राजा बनाया गया?
17. घटवाल विद्रोह झारखंड के किस क्षेत्र में हुवा था?
18. बिरसा मुंडा तकनीकी छात्रवृत्ति योजना किस समुदाय के विद्यार्थियों के लिए हैं?
19. झारखंड की पहली ताप विद्युत गृह कहां बनाई गई?
20. झारखंड की पहली जल विद्युत गृह कहां बनाई गई?
Sunday, 30 May 2021
असुर जातीय शासन व्यवस्था|Asur Administration System|असुर जनजाति सामान्य ज्ञान|Asur General Knowledge
Saturday, 8 May 2021
Jharkhand GK OBJECTIVE
नदी के किनारे बसे शहर
City River Country Adelaide Torrens Australia Al-Cairo Nile Egypt Alexandria Nile Egypt Amsterdam Amsel Netherlands Ankara Kazil Turkey Bag...
-
असुर जातीय शासन व्यवस्था|Asur Administration System|असुर जनजाति सामान्य ज्ञान|Asur General Knowledgeपरिचय असुर समुदाय झारखंड की सबसे प्राचीन जनजाति है। इसका प्रवेश झारखंड में मध्य प्रदेश और छत्तीसगढ़ होते हुए हुआ है। भ...
-
परिचय - पुराने जमाने में देवघर बैजनाथ मठ के रूप में जाना जाता था। देवघर को झारखंड की सांस्कृतिक राजधानी कहा जाता है। ...
-
City River Country Adelaide Torrens Australia Al-Cairo Nile Egypt Alexandria Nile Egypt Amsterdam Amsel Netherlands Ankara Kazil Turkey Bag...
